

|
| Apache Geronimo > Index > Development > XML Schemas > Apache Geronimo v3.0 XML Schemas | User List | Dev List | Wiki | Issue Tracker |
|
Documentation for geronimo-application-client-2.0Table of ContentsSchema Document Properties
Declared Namespaces
Schema Component Representation
<xs:schema
targetNamespace="http://geronimo.apache.org/xml/ns/j2ee/application-client-2.0" elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified" version="1.0">
<xs:import
namespace="http://geronimo.apache.org/xml/ns/naming-1.2" schemaLocation="geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd"/>
<xs:import
namespace="http://geronimo.apache.org/xml/ns/security-2.0" schemaLocation="geronimo-security-2.0.xsd"/>
<xs:import
namespace="http://geronimo.apache.org/xml/ns/j2ee/connector-1.2" schemaLocation="geronimo-connector-1.2.xsd"/>
<xs:import
namespace="http://geronimo.apache.org/xml/ns/deployment-1.2" schemaLocation="geronimo-module-1.2.xsd"/>
... </xs:schema>Global DeclarationsElement: application-client
XML Instance Representation
<geronimo:application-client>
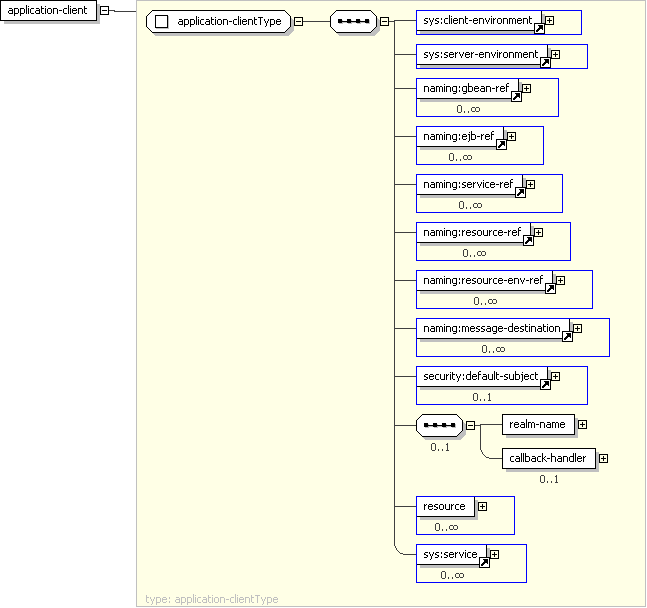
<sys:client-environment> ... </sys:client-environment> [1]
'Reference to client-environment element defined in imported \"geronimo-module-1.2.xsd\"' <sys:server-environment> ... </sys:server-environment> [1]
'Reference to server-environment element defined in imported \"geronimo-module-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:gbean-ref> ... </naming:gbean-ref> [0..*]
'Reference to gbean-ref element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:ejb-ref> ... </naming:ejb-ref> [0..*]
'Reference to ejb-ref element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:service-ref> ... </naming:service-ref> [0..*]
'Reference to service-ref element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:resource-ref> ... </naming:resource-ref> [0..*]
'Reference to resource-ref element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:resource-env-ref> ... </naming:resource-env-ref> [0..*]
'Reference to resource-env-ref element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:message-destination> ... </naming:message-destination> [0..*]
'Reference to message-destination element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <security:default-subject> ... </security:default-subject> [0..1]
Start Sequence
[0..1]
'Reference to default-subject element defined in imported \"geronimo-security-2.0.xsd\" This is the subject run under if you are not logged in.' <geronimo:realm-name>
xs:string </geronimo:realm-name> [1]
'The realm-name element names the security realm used for JAAS login' <geronimo:callback-handler>
xs:string </geronimo:callback-handler> [0..1]
End Sequence
'The callback-handler element specifies the name of a callback class provided by the application for JAAS authentication. This class must implement the javax.security.auth.callback.CallbackHandler interface and follow its specification, as this class will be used by the application client container to collect authentication information from the user.' <geronimo:resource>
geronimo:resourceType
</geronimo:resource> [0..*]
'The resource element names contains the definition of all the module-scoped connector resources. The connector resource can be both external and internal to the application client.' <sys:service> ... </sys:service> [0..*]
</geronimo:application-client>'Reference to service element defined in imported \"geronimo-module-1.2.xsd\"'
Diagram
Schema Component Representation
Global DefinitionsComplex Type: application-clientType
XML Instance Representation
<...>
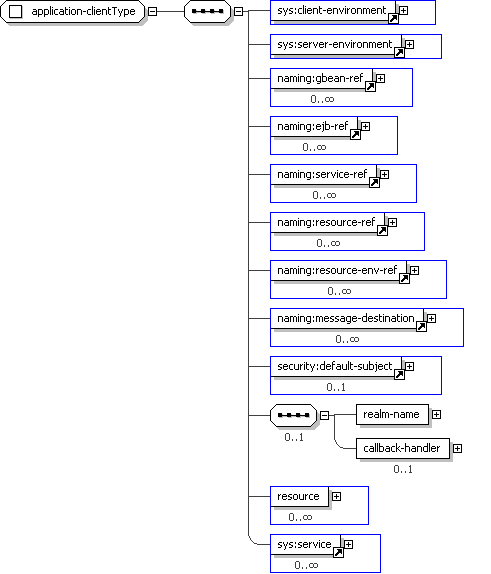
<sys:client-environment> ... </sys:client-environment> [1]
'Reference to client-environment element defined in imported \"geronimo-module-1.2.xsd\"' <sys:server-environment> ... </sys:server-environment> [1]
'Reference to server-environment element defined in imported \"geronimo-module-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:gbean-ref> ... </naming:gbean-ref> [0..*]
'Reference to gbean-ref element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:ejb-ref> ... </naming:ejb-ref> [0..*]
'Reference to ejb-ref element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:service-ref> ... </naming:service-ref> [0..*]
'Reference to service-ref element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:resource-ref> ... </naming:resource-ref> [0..*]
'Reference to resource-ref element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:resource-env-ref> ... </naming:resource-env-ref> [0..*]
'Reference to resource-env-ref element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <naming:message-destination> ... </naming:message-destination> [0..*]
'Reference to message-destination element defined in imported \"geronimo-naming-1.2.xsd\"' <security:default-subject> ... </security:default-subject> [0..1]
Start Sequence
[0..1]
'Reference to default-subject element defined in imported \"geronimo-security-2.0.xsd\" This is the subject run under if you are not logged in.' <geronimo:realm-name>
xs:string </geronimo:realm-name> [1]
'The realm-name element names the security realm used for JAAS login' <geronimo:callback-handler>
xs:string </geronimo:callback-handler> [0..1]
End Sequence
'The callback-handler element specifies the name of a callback class provided by the application for JAAS authentication. This class must implement the javax.security.auth.callback.CallbackHandler interface and follow its specification, as this class will be used by the application client container to collect authentication information from the user.' <geronimo:resource>
geronimo:resourceType
</geronimo:resource> [0..*]
</...>'The resource element names contains the definition of all the module-scoped connector resources. The connector resource can be both external and internal to the application client.'
Diagram
Schema Component Representation
<xs:complexType
name="application-clientType">
<xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType><xs:sequence
minOccurs="0">
</xs:sequence>
</xs:sequence>Complex Type: resourceType
XML Instance Representation
<...>
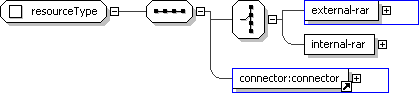
Start Choice [1] <geronimo:external-rar>
sys:patternType
</geronimo:external-rar> [1]
'The external-rar is a Module ID of the resource adapter in the Geronimo repository.' <geronimo:internal-rar>
xs:string </geronimo:internal-rar> [1]
End Choice
'The internal-rar is a Module ID of the resource adapter in the client module.' </...>
Diagram
Schema Component Representation
<xs:complexType
name="resourceType">
<xs:sequence> </xs:complexType><xs:choice>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>LegendComplex Type:Schema Component Type
AusAddressSchema Component Name
If this schema component is a type definition, its type hierarchy is shown in a gray-bordered box.
The table above displays the properties of this schema component.
XML Instance Representation
<...
country="Australia"
>
<unitNo> string </unitNo> [0..1] <houseNo> string </houseNo> [1] <street> string </street> [1] Start Choice [1] <city> string </city> [1] <town> string </town> [1] End Choice <state> AusStates </state> [1] <postcode> string <<pattern = [1-9][0-9]{3}>> </postcode> [1] </...> The XML Instance Representation table above shows the schema component's content as an XML instance.
Schema Component Representation
<complexType
name="AusAddress">
<complexContent> <extension base=" Address "> <sequence> <element name="state" type=" AusStates "/> <element name="postcode"> <simpleType> <restriction base=" string "> <pattern value="[1-9][0-9]{3}"/> </restriction> </simpleType> </element> </sequence> <attribute name="country" type=" string " fixed="Australia"/> </extension> </complexContent> </complexType> The Schema Component Representation table above displays the underlying XML representation of the schema component. (Annotations are not shown.)
GlossaryAbstract (Applies to complex type definitions and element declarations). An abstract element or complex type cannot used to validate an element instance. If there is a reference to an abstract element, only element declarations that can substitute the abstract element can be used to validate the instance. For references to abstract type definitions, only derived types can be used. All Model Group Child elements can be provided in any order in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-all. Choice Model Group Only one from the list of child elements and model groups can be provided in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-choice. Collapse Whitespace Policy Replace tab, line feed, and carriage return characters with space character (Unicode character 32). Then, collapse contiguous sequences of space characters into single space character, and remove leading and trailing space characters.
Disallowed Substitutions
(Applies to element declarations). If substitution is specified, then substitution group members cannot be used in place of the given element declaration to validate element instances. If derivation methods, e.g. extension, restriction, are specified, then the given element declaration will not validate element instances that have types derived from the element declaration's type using the specified derivation methods. Normally, element instances can override their declaration's type by specifying an Key Constraint Like Uniqueness Constraint, but additionally requires that the specified value(s) must be provided. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions. Key Reference Constraint Ensures that the specified value(s) must match value(s) from a Key Constraint or Uniqueness Constraint. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions. Model Group Groups together element content, specifying the order in which the element content can occur and the number of times the group of element content may be repeated. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#Model_Groups.
Nillable
(Applies to element declarations). If an element declaration is nillable, instances can use the Notation A notation is used to identify the format of a piece of data. Values of elements and attributes that are of type, NOTATION, must come from the names of declared notations. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cNotation_Declarations. Preserve Whitespace Policy Preserve whitespaces exactly as they appear in instances. Prohibited Derivations (Applies to type definitions). Derivation methods that cannot be used to create sub-types from a given type definition. Prohibited Substitutions (Applies to complex type definitions). Prevents sub-types that have been derived using the specified derivation methods from validating element instances in place of the given type definition. Replace Whitespace Policy Replace tab, line feed, and carriage return characters with space character (Unicode character 32). Sequence Model Group Child elements and model groups must be provided in the specified order in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-sequence. Substitution Group Elements that are members of a substitution group can be used wherever the head element of the substitution group is referenced. Substitution Group Exclusions (Applies to element declarations). Prohibits element declarations from nominating themselves as being able to substitute a given element declaration, if they have types that are derived from the original element's type using the specified derivation methods. Target Namespace The target namespace identifies the namespace that components in this schema belongs to. If no target namespace is provided, then the schema components do not belong to any namespace. Uniqueness Constraint Ensures uniqueness of an element/attribute value, or a combination of values, within a specified scope. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions. |